Enhancing File Upload Security in .NET Core with File Signature Validation
Why Use File Signature Validation? —
- Prevents Spoofing Attacks — Attackers may rename a file (e.g., .exe to .jpg) to bypass extension-based filtering.
- Stops Malware Uploads — Ensures that only legitimate file types are processed and prevents execution of malicious scripts.
- Improves Data Integrity — Helps detect tampered files before they are stored or executed.
- Enhances Compliance — Many regulatory standards (e.g., PCI DSS, HIPAA) require secure file handling.
How File Signature Validation Works —
Extract File Signature —
- Every file format has a unique binary signature (also called "magic number") at the beginning of the file.
- This signature is compared against a list of allowed file types.
Validate Against Expected Format: —
- Check if the extracted signature matches the expected format.
- If the signature doesn't match the extension, reject the upload.
Perform Additional Security Checks
- Virus Scanning: Use an antivirus engine to scan files.
- Size Restrictions: Set limits to prevent DoS attacks via large file uploads.
- Content-Type Verification: Ensure that the MIME type matches the file's actual content.
Steps to Implement File Signature Validation in .NET Core
Define Allowed File Signatures: -
Each file type has a unique signature (byte sequence) at the beginning of the file. Below are some common file signatures:
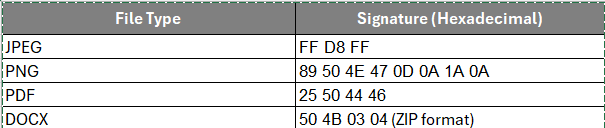
Define a dictionary to map file types to their signatures:
public static class FileSignatures
{
public static readonly Dictionary<string, List<byte[]>> Signatures = new()
{
{ ".jpg", new List<byte[]> { new byte[] { 0xFF, 0xD8, 0xFF } } },
{ ".png", new List<byte[]> { new byte[] { 0x89, 0x50, 0x4E, 0x47, 0x0D, 0x0A, 0x1A, 0x0A } } },
{ ".pdf", new List<byte[]> { new byte[] { 0x25, 0x50, 0x44, 0x46 } } },
{ ".docx", new List<byte[]> { new byte[] { 0x50, 0x4B, 0x03, 0x04 } } } // DOCX is a ZIP file format
};
}
Validate File Signature During Upload: —
Use the file stream to read the first few bytes and compare them against the allowed signatures.
public static bool IsValidFileSignature(Stream fileStream, string fileExtension)
{
if (!FileSignatures.Signatures.ContainsKey(fileExtension))
return false; // File type is not allowed
var allowedSignatures = FileSignatures.Signatures[fileExtension];
using (var reader = new BinaryReader(fileStream))
{
foreach (var signature in allowedSignatures)
{
fileStream.Position = 0; // Reset stream position before reading
var headerBytes = reader.ReadBytes(signature.Length);
if (headerBytes.SequenceEqual(signature))
return true; // Valid file signature
}
}
return false; // Invalid file signature
}
Implement File Validation in Controller : —
Modify the file upload controller to validate the file signature before saving.
[HttpPost("upload")]
public async Task<IActionResult> UploadFile(IFormFile file)
{
if (file == null || file.Length == 0)
return BadRequest("File is empty.");
var extension = Path.GetExtension(file.FileName).ToLowerInvariant();
using var fileStream = file.OpenReadStream();
if (!IsValidFileSignature(fileStream, extension))
return BadRequest("Invalid file format.");
var filePath = Path.Combine("Uploads", file.FileName);
using (var stream = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.Create))
{
await file.CopyToAsync(stream);
}
return Ok("File uploaded successfully.");
}